Gold Plating Services per MIL-G-45204, ASTM B488, AMS 2422
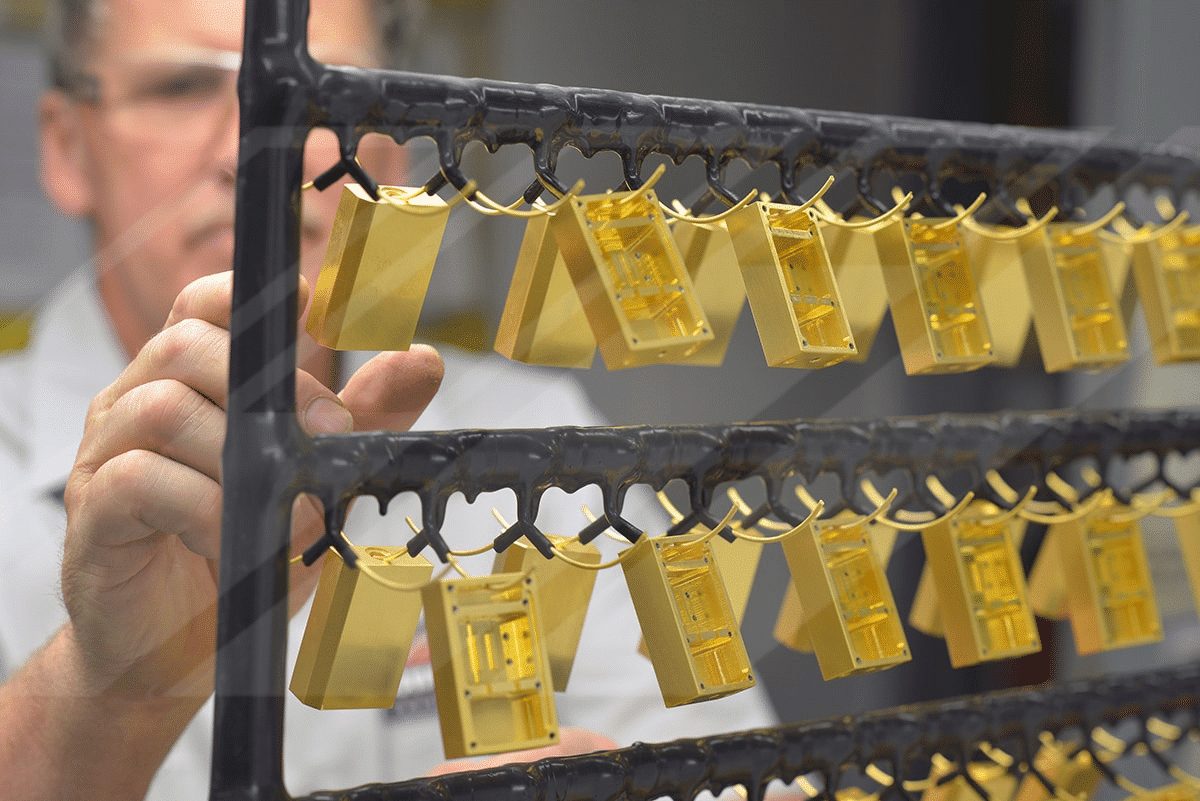
Advanced Plating Technologies (APT) is an industry leading metal finishing company that provides functional gold electroplating to MIL-G-45204, ASTM B488 or AMS 2422. Our over seventy five years of expertise in providing precision “loose piece” barrel, rack and vibratory gold plating is currently employed in numerous industries including the medical, telecommunications, aerospace, defense and electronics industries.
APT offers functional gold electroplating in 99.7% (Type I and II) hard gold and 99.9% (Type III) pure soft gold electrodeposits. Hard gold services are commonly employed in applications where repeated sliding or connection wear is a design consideration, such as in female to male interconnect pins or spring contacts. APT offers hard gold electroplating that is alloyed with a small amount of nickel to achieve the required deposit properties. Soft gold is more commonly used in high temperature, wire bonding or biocompatible applications where the highest possible gold purity is beneficial.
Advanced Plating Technologies has the ability to underplate gold with our various nickel plating services including both bright electrolytic nickel, sulfamate electrolytic nickel and electroless nickel deposits as well as copper plating or silver plating if required. The appearance of gold plating is very much a function of the underplate that is applied prior to deposition of the final gold layer. If a unbrightened nickel such as sulfamate nickel is applied, the gold deposit will have less overall luster. If a bright electrolytic nickel or medium phosphorus electroless nickel is utilized, the gold will have a brighter appearance. As with any deposit, the surface finish of the raw material has a significant impact on the appearance of the final finish.

ISO 13485:2016

ITAR Compliant

ISO 9001:2015

Federal Firearms License

ISO 13485:2016

ITAR Compliant

ISO 9001:2015

Federal Firearms License
SELECT ONE TO LEARN MORE
Benefits of Gold Plating
Hard vs Soft Gold Plating
Gold Plating Thickness of Connectors
Gold vs Silver Connectors

|
Gold |
AURUM |
| Atomic Number – Qty Protons: | 79 | Thermal Conductivity – W/(cm*K): | 3.17 |
| Atomic Weight – g/mole: | 197 | Electrical Resistivity – nOhm*m: | 22.14 |
| Density – g/cm3: | 19.3 | Hardness – Hv: | 216 Hv |
| Melting Point – C°: | 1064 | Specific Heat Capacity – J/(g*K): | 0.13 |
Gold is a precious metal that has excellent electrical and thermal conductivity, offers exceptional solderability and is a superb reflector of infrared radiation. In addition, gold is a noble metal that does not oxidize or chemically react under normal conditions. For this reason, gold is an exceptional choice for engineering requirements where electrical conductivity (especially at low voltages), solderability and corrosion resistance are design requirements.
Gold is a very dense, soft and malleable metal with excellent ductility. It is one of the least reactive chemical elements second only to Platinum in reactivity. Gold is resistant to most mineral and oxidizing acids and can only be dissolved in aqua regia or alkaline cyanide solutions. Due to its stable nature, pure gold is found in nuggets, veins and alluvial deposits throughout the earth. The yellow-orange color of gold is instantly recognizable and has been valued since antiquity for its appearance and noble properties. In recent years, the use of gold in industry has seen a surge due to the Internet of Things (IoT) and overall increase in use of electrical and interconnect components including quantum computing.


|
Gold |
AURUM |
| Atomic Number – Qty Protons: | 79 | Thermal Conductivity – W/(cm*K): | 3.17 |
| Atomic Weight – g/mole: | 197 | Electrical Resistivity – nOhm*m: | 22.14 |
| Density – g/cm3: | 19.3 | Hardness – Hv: | 216 Hv |
| Melting Point – C°: | 1064 | Specific Heat Capacity – J/(g*K): | 0.13 |

Gold
AURUM

| Atomic Number – Qty Protons: | 79 |
| Thermal Conductivity – W/(cm*K): | 3.17 |
| Atomic Weight – g/mole: | 197 |
| Electrical Resistivity – nOhm*m: | 22.14 |
| Density – g/cm3: | 19.3 |
| Hardness – Hv: | 216 Hv |
| Melting Point – C°: | 1064 |
| Specific Heat Capacity – J/(g*K): | 0.13 |
Gold Deposit Properties
old has excellent electrical and thermal conductivity, offers exceptional solderability and is a superb reflector of infrared radiation. In addition, gold is a noble metal that does not oxidize or chemically react under normal conditions. For this reason, gold is an exceptional choice for numerous engineering requirements where electrical conductivity (especially at low voltages), solderability and corrosion resistance are design requirements.
Advanced Plating Technologies, a Milwaukee, Wisconsin company, offers gold plating in both 99.7% pure “hard” gold and 99.9% pure soft gold electrodeposits. Hard gold services are commonly employed in applications where repeated sliding or connection wear is a design consideration, such as in female to male interconnect pins or sprung contacts. Our company offers hard gold electroplating that is alloyed with a small amount of cobalt to achieve the required deposit properties.
Soft gold is commonly used where the highest of gold purity is required for soldering, wire bonding, high temperature or high corrosion resistance applications. The soft layer of gold plating deposit provides an extremely pure deposit of gold, which maintains the low hardness, and high corrosion resistance of gold consistent with its elemental form. Soft gold is preferred for high temperature applications due to the fact that alloying elements of hard gold can oxidize at elevated temperatures.
The appearance of gold plating is very much a function of the underplate that is applied prior to deposition of the final gold layer. If a matte nickel such as sulfamate nickel is applied, the final gold deposit will have more of a matte appearance. If a brightened nickel such as bright electrolytic nickel is utilized, the gold will have a bright appearance. As with any deposit, the luster of the basis material has a large degree of correlation to the luster of the final gold plating.
Advanced Plating Technologies’ – Gold Plating Capabilities
Specifications
MIL-G-45204
ASTM B488
AMS 2422
Most Company Specifications
Purity
Soft Gold up to 99.9% Pure
Hard Gold up to 99.7% Pure
Finish Type
Hard (Code B or C per ASTM B488 or Mil-G-45204)
Soft (Code A per ASTM B488 or Mil-G-45204)
Part Size Limitations
24 inches x 22 inches x 10 inches
Substrates Plated On
Ferrous: All Ferrous Alloys Including Mild Steel, Stainless Steels, Hardened Steels & Tool Steels
Cuprous: All Cuprous Alloys Including Pure Copper, Copper Alloys Including Tellurium & Beryllium, Brass, Nickel-Silver
Aluminum: All Aluminum Alloys Including Wrought, Cast and Proprietary Alloys (MIC-6)
Exotics: Inconel, Pure Nickel (Nickel 200), Cobalt-Chrome (MP35N), Kovar, Monel, Hastalloy, Monel, Lead
Underplates Provided
Bright Electrolytic Nickel
Sulfamate Electrolytic Nickel
Electroless Nickel (High or Medium Phosphorous)
Copper
Silver
Heat Treatments
Hydrogen Embrittlement Bakes
Stress Relieving Bakes
High Temp up to 750F
Methods
Selective Loose Piece Plating
Sheet Product (Chemically Milled/Etched Sheets)
Segmented Strips (Frets)
Barrel
Rack
Wire
Vibratory
CONTACT BY EMAIL NOW
Gold Plating Specifications
The three most common gold plating services certified by Advanced Plating Technologies are MIL-G-45204, ASTM B488 and AMS 2422. Our company can provide Type I, II and III gold deposits per these industry standards. Gold plating services to AMS 2425 as well as most company-specific gold specifications can also be provided as detailed in our specification database. A summary of gold plating services to ASTM B488, MIL-G-45204 and AMS 2422 is provided below:

Gold Plating Services to ASTM B488-01
Note: ASTM B488 underwent a major revision from 1995 to 2001. The Type callout of the ASTM was revised to parallel that of MIL-G-45204 such that the Type and Codes of the ASTM and MIL specs are synonymous. The Types listed below are per the current 2001 revision of ASTM B488.
Type I: 99.7% pure gold with a hardness ranging from A (90 HK25 max) to C (130-200 HK25).
Type II: 99.0% pure gold often referred to as hard gold with a hardness ranging from B (91-129 KH25) to D (> 200 HK25).
Type III: 99.9% pure gold often referred to as soft gold with a hardness of A only (90 HK25 Max).
Code A: 90 HK25 Maximum
Code B: 91-129 HK25
Code C: 130-200 HK25
Code D: > 200 HK25
Relationship Between Purity and Hardness (ASTM B488-01 and Newer)
Type Code
I A, B and C
II B, C and D
III A Only
Class Minimum Thickness [um/uin]
0.25 – 0.25um (~ 10uin)
0.50 – 0.50um (~ 20uin)
0.75 – 0.75um (~ 30uin)
1.0 – 1.0um (~ 40uin)
1.25 – 1.25um (~ 50uin)
2.5 – 2.5um (~ 100uin)
5.0 – 5.0um (~ 200uin)
6.5.1 Nickel Underplating – For thickness classes except 5.0, a nickel underplating shall be applied before the gold coating when the product is made from copper or copper alloy. Nickel Underplating is also applied for other reasons (see Appendix X6).
Appendix X6: Some Reasons for Using a Nickel Underplate
X6.1 Diffusion Barrier (E.g. migration of zinc into the gold layer from a brass substrate)
X6.2 Leveling Layer (Brightening)
X6.3 Pore Corrosion Inhibitor
X6.4 Tarnish Creepage Inhibitor for Gold
X6.5 Load-Bearing Underlayer for Contacting Surfaces

Gold Plating Services to MIL-G-45204
Type I – 99.7 percent gold minimum
Type II – 99.0 percent gold minimum
Type III – 99.9 percent gold minimum
Grade A – Knoop hardness 90 max
Grade B – Knoop hardness 91-129, incl.
Grade C – Knoop hardness 130-200, incl.
Grade D – Knoop hardness 201 and over.
If the hardness grade for the gold coating is not specified, Type I shall be furnished at hardness Grade A (90 Knoop max) and Type II shall be furnished at hardness Grade C (130 to 200 Knoop)
Purity (Type) and hardness (grade) relationship:
Purity Hardness
Type I A, B or C
Type II B, C or D
Type III A only
Class 00 – 0.00002 inch thick, minimum
Class 0 – 0.00003 inch thick, minimum
Class 1 – 0.00005 inch thick, minimum
Class 2 – 0.00010 inch thick, minimum
Class 3 – 0.00020 inch thick, minimum
Class 4 – 0.00030 inch thick, minimum
Class 5 – 0.00050 inch thick, minimum
Class 6 – 0.00150 inch thick, minimum
Underplate Requirements per section 6.3: a copper, nickel, or copper plus nickel underplate may be used, depending on the application and the environment. Silver or copper plus silver may not be used unless required by item specification. A soft gold strike from a separate plating tank should follow any other undercoating and precede the final gold coating to improve adhesion and prevent contamination of the main gold plating solution by metallic impurities. When applied to a copper rich surface such as brass, bronze or beryllium copper or a copper plate or strike, an anti-diffusion underplate such as nickel shall be applied.


Gold Plating Services to AMS 2422
3.2.1 Copper Flash or Copper Strike: A copper flash or copper strike shall be electrodeposited from a suitable plating solution, except as exempted in 3.2.1.1.
3.2.1.1 When parts to be plated are made of copper or copper alloy containing less than 15% zinc, the copper flash or copper strike may be omitted.
3.2.2 Nickel Flash or Nickel Strike: A nickel flash or nickel strike shall be electrodeposited from a suitable nickel plating solution over the copper, copper alloy containing less than 15% zinc, copper flash or copper strike as applicable.
3.4.1.1 Copper Flash or Strike: Not less than 0.0001 inch (2.5um)
3.4.1.2 Nickel Strike: Not less than 0.0001 inch (2.5um)
3.4.1.3 Gold Plate: Note less than 0.00005 inch (1.27um) on all surfaces on which gold plating is specified.
3.4.4 Purity: Gold, as plated, shall be not less than 99.0% pure, determined by a method acceptable to purchaser.