A Family of High-Performance nickel barrier coatings engineered for steel penetrator projectiles. The Dura-Nickel family of coatings were engineered to solve the corrosion performance shortfall of a sacrificial zinc coating on a steel penetrator
The coating requirements specified a finish must:
- Provide assembled salt spray performance up to 96-Hrs without degradation of either hard or soft target performance
- Maintain extreme concentric uniformity with a weight variation of less than +/- 0.25 grains
- Ensure durability in mass handling, high pressure bullet assembly, rapid production SCAMP loading and linking
Next Generation Nickel Systems Modern Ammunition Applications
Traditional ammunition systems have not changed their principal materials of manufacture since the late 19th century. However, the construction of advanced, next-generation ammunition systems has evolved in recent years utilizing new materials including steel alloys, stainless steel, tungsten and even polymers. This change has expanded the performance envelop, significantly improving both ballistics and terminal performance while reducing cartridge weight. New materials require component surfaces to be properly engineered, specifically at the areas of engagement. This is especially important when the materials in the design are further apart in the electromotive series, and therefore more likely to react and corrode with one another. An example of this design consideration is in the use of exposed steel penetrators formed within a copper projectile. Coatings such as zinc have been used to delay corrosion of the steel penetrator. However, these sacrificial coatings have severe limitations that result in premature formation of white corrosion products even in moderate service conditions.
Performance Advantages of Dura-Nickel
The performance advantages of Dura-Nickel can be leveraged within a range of ammunition applications including hybrid or steel case designs and improved corrosion resistance over traditional nickels on standard brass or gilding metal.
Dura-Nickel HP+® is a more cost-effective coating that can be used in most applications where radii of the components can be maintained at 0.020” or greater.
Dura-Nickel A1™ is a next-generation coating within the Dura-Nickel family that provides improved corrosion resistance, especially in applications where sharp tips and radii of components are less than 0.020”.
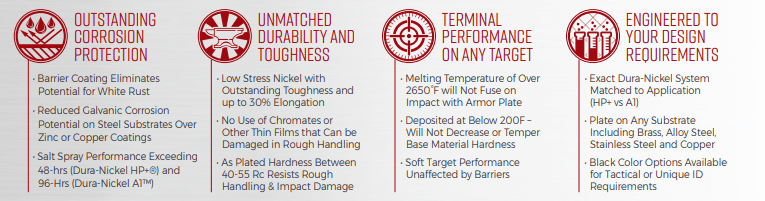
Outstanding corrosion protection: Barrier Coating Eliminates Potential for White Rust, Reduced Galvanic Corrosion Potential on Steel Substrates Over Zinc or Copper Coatings, and Salt Spray Performance Exceeding 48-hrs (Dura-Nickel HP+®) and 96-Hrs (Dura-Nickel A1™)

Terminal Performance on any Target: Melting Temperature of Over 2650°F will Not Fuse on Impact with Armor Plate, Deposited at Below 200F – Will Not Decrease or Temper Base Material Hardness, and Soft Target Performance Unaffected by Barriers
Engineered to your design: Exact Dura-Nickel System Matched to Application (HP+ vs A1), Plate on Any Substrate Including Brass, Alloy Steel, Stainless Steel and Copper, and Black Color Options Available for Tactical or Unique ID Requirements
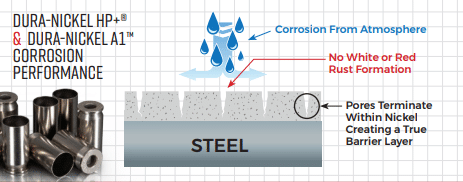
Sacrificial vs. Barrier Corrosion Protection – What is the Difference?
Corrosion resistance coatings fall into two primary categories – sacrificial or barrier coatings. The difference between the two lies in if the coating is more or less likely to corrode than the base